Morocco, a culturally diverse country, boasts multiple official languages that contribute to its vibrant linguistic landscape. With language playing a crucial role in shaping the identity of its people, Morocco embraces a variety of communication channels and terms across different areas. The use of these official languages extends beyond everyday interactions to encompass domains such as education, technology, science, and even legal matters like the drafting of the country’s charter. This linguistic diversity reflects both historical influences and contemporary realities, making Morocco an intriguing case study for language scholars and enthusiasts alike.
Official Languages of Morocco

Arabic Dominance
Arabic holds a dominant position as the official language in Morocco. It is widely used in various formal settings, including government institutions, education, and media. Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) is commonly employed in these contexts, ensuring linguistic consistency and facilitating communication among different regions of the country. However, it is important to note that Moroccan Arabic (Darija) is the most commonly spoken dialect among the population.
The prevalence of Arabic can be attributed to historical factors and cultural influences. As Morocco has a rich Arab heritage, with significant Arab migrations throughout history, the language has become deeply ingrained in society. While MSA serves as a unifying force for written and formal communication, Darija reflects the everyday language used by Moroccans in their daily interactions.
Tamazight Recognition
In recent years, there has been an increasing recognition of Tamazight as an official language in Morocco. Tamazight belongs to the Berber language family and holds great significance for the indigenous Berber population of Morocco. Efforts have been made to preserve and promote this ancient language through its inclusion in educational curricula and official documents.
The recognition of Tamazight as an official language represents a significant step towards acknowledging and valuing linguistic diversity within Morocco. It not only provides recognition for the cultural heritage of Berber communities but also promotes inclusivity by giving them a platform to express their identity through their native tongue.
Language Policy
Morocco’s language policy aims at striking a balance between linguistic diversity and national unity. The government recognizes that embracing multiple languages contributes to social cohesion while preserving cultural heritage.
To achieve this goal, bilingualism and multilingual education are promoted across schools and universities throughout the country. Students are encouraged to learn both Arabic (MSA) and French – another influential language due to historical ties with former colonial powers – alongside their mother tongue or regional dialect.
Over time, Morocco’s language policies have evolved to address the needs of its society. By recognizing Tamazight as an official language and promoting multilingual education, the government has taken significant steps toward fostering inclusivity and preserving linguistic diversity within the country.
Arabic in Morocco

Varieties of Arabic
Different regions in Morocco have distinct varieties of Arabic. This is due to the country’s diverse cultural and historical influences. Moroccan Arabic, also known as Darija, is the most widely spoken form of Arabic in the country. However, it is important to note that Moroccan Arabic incorporates elements from other languages like French and Spanish.
The various regional variations of Arabic in Morocco can pose challenges for effective communication. Each region has its own unique dialect with specific vocabulary, pronunciation, and grammar. For example, in the Middle Atlas region, a Berber dialect called Tamazight is spoken alongside Arabic.
To navigate these linguistic differences, it is crucial to understand the regional variations when communicating with locals. This can help build rapport and avoid misunderstandings. Learning some basic phrases or expressions specific to a particular region can go a long way in establishing connections and showing respect for local culture.
Classical and Modern Standard
In addition to the regional variations of Arabic, Morocco also recognizes Classical Arabic and Modern Standard Arabic as official languages.
Classical Arabic holds great significance as it is used primarily in religious and literary contexts. It serves as the language of the Quran and remains an integral part of Islamic scholarship. While not commonly spoken in everyday conversations, knowledge of Classical Arabic allows individuals to engage with religious texts and participate in religious ceremonies.
On the other hand, Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) serves as the written standard for formal communication across Arab countries including Morocco. It is used in areas such as government documents, newspapers, literature, education materials, and formal speeches.
Both Classical and Modern Standard Arabic are taught in schools throughout Morocco. Students receive instruction on reading and writing using MSA while also learning about classical literature and poetry.
While MSA provides a common ground for formal communication among Arabs from different countries, it may still differ slightly from Moroccan dialects spoken on a daily basis. Therefore, understanding the differences between MSA and Moroccan Arabic is crucial to effectively communicate in various contexts.
Berber Language in Morocco
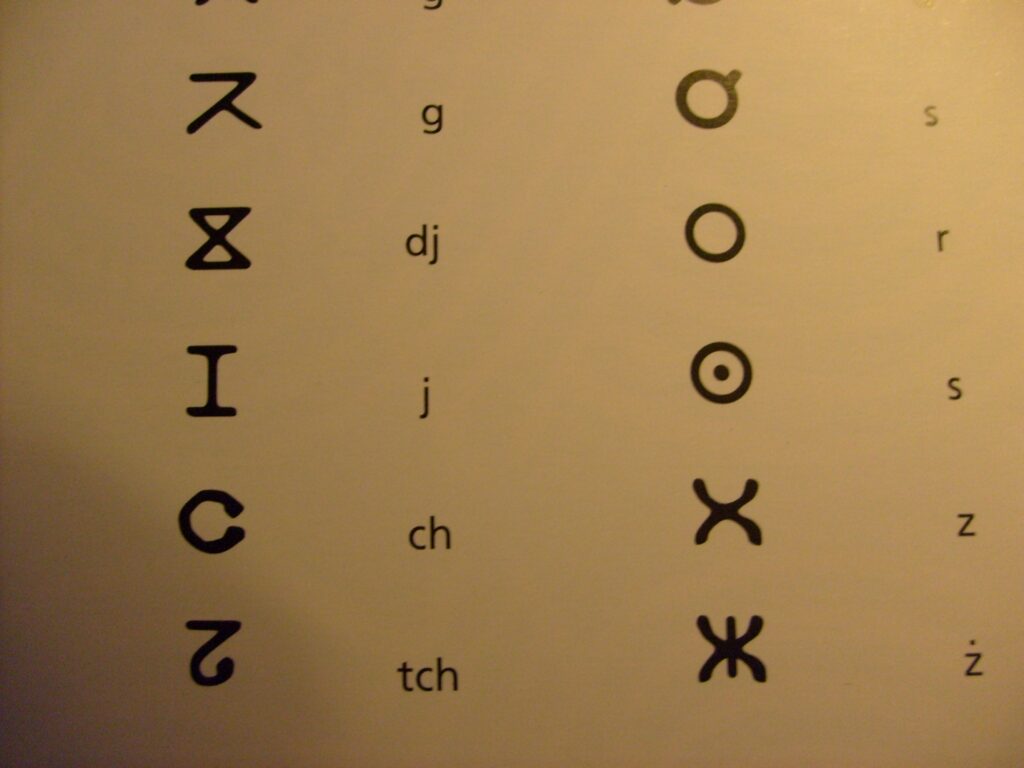
Tamazight Status
Tamazight, one of the Berber languages, has gained official status alongside Arabic in Morocco. It is recognized as a national language in the country’s constitution. This recognition marks an important step towards promoting linguistic diversity and inclusivity within Moroccan society.
Efforts are being made to integrate Tamazight into various aspects of society. The government has implemented policies to ensure its inclusion in education, media, and public administration. Schools now offer Tamazight language classes, allowing students to learn and appreciate their cultural heritage. There are initiatives to translate official documents and road signs into Tamazight, making it more accessible to all Moroccans.
You might find interesting: Berber People: All You Need to Know
Indigenous Identity
The recognition of Tamazight contributes significantly to the preservation of indigenous identity in Morocco. Language plays a vital role in maintaining cultural heritage among indigenous communities. By acknowledging and promoting Tamazight as an official language, the government recognizes the importance of these communities’ history, traditions, and way of life.
Embracing linguistic diversity strengthens the sense of belonging for different groups within Moroccan society. When individuals can express themselves in their native language, they feel a stronger connection to their community and culture. This recognition also empowers indigenous communities by validating their identities and ensuring that their voices are heard.
Furthermore, preserving indigenous languages like Tamazight helps prevent the loss of valuable knowledge and traditional practices that have been passed down through generations. Language serves as a vehicle for transmitting cultural values, beliefs, stories, and customs from one generation to another.
Influence of French and Spanish

Colonial Legacy
During the colonial period, Morocco experienced significant linguistic influence from both French and Spanish. The French protectorate era, which lasted from 1912 to 1956, played a crucial role in shaping Morocco’s linguistic landscape. As a result, French became widely spoken and continues to be used as an official language alongside Arabic.
The impact of colonialism can still be observed in various aspects of Moroccan society, including language use and education. Many Moroccans today are bilingual or even multilingual, with proficiency in Arabic, French, and sometimes Spanish. This linguistic diversity is a testament to the enduring legacy of colonial rule.
Bilingualism and Education
Bilingual education is highly encouraged in Morocco to foster multilingualism and promote cultural exchange. Arabic serves as the primary language of instruction in schools across the country. However, due to the historical influence of the French during the colonial era, it also holds significant importance in the education system.
French is taught as a second language from an early age and is commonly used for subjects such as mathematics and science. This approach aims to provide students with proficiency in Arabic and French, enabling them to access a broader range of educational resources and opportunities.
Efforts are also being made to incorporate Tamazight, the Berber language spoken by indigenous communities in Morocco, into the education system. Recognizing its cultural significance and value, steps have been taken to introduce Tamazight as an optional subject at various levels of schooling. This initiative seeks to preserve and promote indigenous languages alongside Arabic and French.
Judeo-Spanish and Minority Languages
Historical Presence
Arabic has a long historical presence in Morocco, dating back to the arrival of Arab conquerors. The Arabization process began centuries ago and gradually took hold in Moroccan society. Over time, Arabic became deeply rooted, both linguistically and culturally.
Language Preservation
Efforts to preserve languages aim to safeguard linguistic diversity and contribute to the conservation of cultural heritage. In Morocco, initiatives are underway to document endangered languages, including Judeo-Spanish and various minority languages.
Judeo-Spanish, also known as Ladino, is a language derived from Old Spanish spoken by Sephardic Jews who were expelled from Spain during the Inquisition. Despite its decline due to migration and assimilation over the years, there are still communities in Morocco where Judeo-Spanish is spoken. These communities play an essential role in preserving this unique language through oral traditions and cultural practices.
In addition to Judeo-Spanish, Morocco is home to several minority languages that enrich its linguistic landscape. One example is Tamazight (Berber), which has been spoken for thousands of years by indigenous Amazigh people across North Africa. Efforts have been made to promote Tamazight’s recognition as an official language alongside Arabic.
Other Romance languages such as French and Spanish have also influenced Moroccan culture due to historical ties with former colonial powers. While these languages are not considered official in Morocco, they continue to be widely spoken and used in various domains such as education, business, media, and tourism.
Preserving these different languages is crucial for maintaining cultural diversity within Morocco. It allows for the transmission of unique knowledge systems, traditions, stories, and perspectives across generations. It fosters inclusivity by recognizing the rights of linguistic minorities within society.
Language preservation efforts include documentation projects that aim to record endangered languages before they disappear completely. This involves collecting oral histories, recording conversations, and creating written materials such as dictionaries and grammatical guides. These resources not only serve as valuable references for future generations but also contribute to academic research and linguistic studies.
Education and Language Policy

Curriculum Design
Curriculum design in Morocco reflects the importance of multiple languages. The Moroccan education system recognizes Arabic, French, and Tamazight as official languages, and they are integrated into different subjects throughout the curriculum. This approach promotes multilingualism and cultural understanding among students.
In Morocco, language learning is not limited to a single subject or class; it is infused into various disciplines such as science, mathematics, history, and literature. For example, students may study scientific concepts in Arabic while also learning about the historical context in French or Tamazight. This comprehensive integration of languages allows students to develop proficiency in multiple languages simultaneously.
By incorporating different languages into the curriculum, Morocco aims to equip its students with strong language skills and foster cultural awareness. Students gain a deeper understanding of diverse cultures and perspectives through exposure to various linguistic traditions. This approach prepares them for a globalized world where cross-cultural communication is increasingly important.
Multilingual Education
Multilingual education plays a crucial role in enhancing language skills and promoting cultural awareness among Moroccan students. By learning multiple languages from an early age, students develop strong linguistic abilities that can benefit them academically and professionally.
In Moroccan schools, multilingualism is encouraged through immersion programs where students are exposed to Arabic, French, and Tamazight on a daily basis. This immersive approach helps learners acquire language skills naturally by using them in real-life contexts. It also fosters an appreciation for linguistic diversity within the country.
Moreover, multilingual education prepares Moroccan students for international opportunities by equipping them with the necessary language proficiency to engage with people from different backgrounds. In an increasingly interconnected world, being able to communicate effectively across borders is a valuable skill that opens doors to academic pursuits, career prospects, and cultural exchanges.
The emphasis on multilingual education aligns with Morocco’s commitment to promoting linguistic diversity within its society while recognizing the importance of global communication. By nurturing language skills and cultural awareness, the education system aims to empower students to become active participants in an interconnected world.
Population Census and Linguistic Diversity

Demographic Insights
Understanding demographic patterns is crucial in shaping language policies in Morocco. By analyzing statistical figures from population censuses, policymakers gain valuable insights into the linguistic diversity of different regions within the country. These insights inform educational strategies and language planning, ensuring that language policies are tailored to meet the needs of specific communities.
Each region in Morocco has its own unique linguistic composition. The population census helps identify the predominant languages spoken in each area, allowing policymakers to allocate resources effectively. For example, in regions where Amazigh languages are widely spoken, initiatives can be implemented to preserve and promote these languages through education and cultural programs.
Demographic insights also shed light on the distribution of Arabic dialects across different regions. While Modern Standard Arabic is the official language of Morocco, various dialects like Moroccan Arabic (Darija) play a significant role in daily communication. These dialects have evolved over time and reflect the influence of historical interactions with other cultures.
Spoken vs Official Languages
Although Arabic is the official language of Morocco, it is important to recognize that other languages are widely spoken throughout the country. In addition to Moroccan Arabic (Darija), French also holds a prominent position as a second language due to historical ties between Morocco and France.
The recognition of both spoken and official languages is essential for effective interaction within Moroccan society. While Modern Standard Arabic serves as a unifying language for formal settings such as government institutions and education, understanding local dialects facilitates everyday communication among Moroccans from different regions.
Moreover, acknowledging linguistic diversity promotes inclusivity and cultural appreciation within society. It allows individuals to express themselves comfortably in their native tongues while still maintaining proficiency in the official language. This approach fosters social cohesion by valuing all languages present within Moroccan communities.
Online Language Courses in Morocco

E-Learning Growth
E-learning platforms have played a significant role in expanding language learning opportunities in Morocco. With the advancement of technology, online resources have made it easier for individuals to access language courses and materials conveniently. These platforms offer a wide range of interactive tools and multimedia resources that enhance the learning experience.
One of the key advantages of e-learning is its flexibility, allowing learners to study at their own pace. This self-paced approach to language acquisition has proven to be highly effective for many individuals. Students can choose when and where they want to study, making it ideal for those with busy schedules or other commitments.
Language Accessibility
Ensuring language accessibility is crucial for promoting inclusive education in Morocco. Efforts are being made to provide equal opportunities for all learners, regardless of their background or abilities. By embracing e-learning platforms, educational institutions can reach out to diverse communities and ensure that language courses are accessible to everyone.
Online language courses break down barriers by eliminating geographical constraints. Learners from remote areas or regions with limited educational resources can now access quality language instruction through these digital platforms. Moreover, people with physical disabilities who may face challenges attending traditional classroom settings can also benefit from the flexibility offered by e-learning.
Promoting language accessibility not only benefits individuals but also contributes to the overall development of society. When more people have access to education and language learning opportunities, it fosters cultural understanding and communication among different communities within Morocco.
E-learning platforms provide a supportive environment for learners who may feel intimidated or shy in traditional classroom settings. The interactive nature of online courses encourages participation and engagement, creating an inclusive space where students feel comfortable practicing their speaking skills without fear of judgment.
English Usage in Morocco

Global Integration
Language diversity plays a crucial role in enhancing Morocco’s global integration. With multiple official languages, including Arabic, French, and Amazigh, Morocco has positioned itself as a hub for international communication. Proficiency in these languages fosters economic, political, and cultural connections with other countries.
Multilingualism provides numerous advantages for Morocco on the global stage. It enables effective communication with a wide range of nations and facilitates trade relationships. For example, being proficient in Arabic allows Moroccan businesses to engage with countries in the Middle East and North Africa region. Similarly, fluency in French opens doors to economic opportunities with Francophone countries.
Moreover, English proficiency has become increasingly important for global integration. As one of the most widely spoken languages worldwide, English serves as a lingua franca for international communication. By embracing English education and promoting its usage within the country, Morocco can further strengthen its ties with countries across the globe.
Business and Tourism
Language skills are highly valuable for both the business and tourism sectors in Morocco. Given that Arabic is widely spoken throughout North Africa and the Middle East, proficiency in this language is essential for conducting business within these regions. French remains an important language of commerce due to the historical ties between France and Morocco.
However, it is worth noting that English has gained significant importance within the business landscape as well. Many multinational companies operate in Morocco or have partnerships with Moroccan businesses. Therefore, having strong English skills can greatly enhance career prospects within these organizations.
In terms of tourism, effective communication is vital to provide an exceptional visitor experience. Being able to communicate fluently in Arabic allows tourists to immerse themselves more fully in Moroccan culture while interacting with locals during their travels. Furthermore, proficiency in French is advantageous since many tourists from Francophone countries visit Morocco each year.
English proficiency among those working directly or indirectly within the tourism industry also plays a crucial role. It enables them to cater to the needs of English-speaking tourists, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable experience for visitors from around the world.
Historical Summary of Moroccan Languages

Language Evolution
Languages evolve over time due to societal changes and influences. In the case of Morocco, the evolution of languages has been shaped by various factors throughout history. One prominent language in Morocco is Moroccan Arabic, which continues to adapt to new expressions and vocabulary. This evolution reflects the dynamic nature of language and its ability to respond to the changing needs and experiences of its speakers.
Understanding language evolution is essential for effective communication in Morocco. As languages change, new words and phrases emerge, reflecting shifts in culture, technology, and social dynamics. By keeping up with these linguistic developments, individuals can ensure that their communication remains relevant and meaningful within Moroccan society.
Cultural Influence
Language serves as a reflection of the cultural influence on Moroccan society. The linguistic landscape of Morocco is rich and diverse, encompassing multiple languages such as Arabic, Berber dialects, French, and Spanish. Each language contributes to the expression of different aspects of Moroccan culture.
For instance, Arabic is not only a means of communication but also an integral part of Moroccan identity. It carries historical significance as it has been used for centuries in religious texts and literary works. Berber dialects reflect the indigenous heritage of Morocco’s Amazigh population and contribute to preserving their cultural traditions.
Furthermore, France has had a significant impact on Moroccan society due to colonial history. It remains widely spoken today and is crucial in education, administration, business, media, and diplomacy. Spanish influences can be found primarily in certain regions close to Spain.
The presence of multiple languages facilitates cultural exchange within Morocco. Through linguistic interactions between individuals who speak different languages or dialects, ideas are shared, perspectives are broadened, and understanding is deepened. This linguistic diversity enhances the richness of Moroccan culture by fostering inclusivity and encouraging cross-cultural dialogue.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the languages of Morocco reflect the country’s rich linguistic diversity and complex historical influences. Arabic and Berber are the official languages, with French and Spanish also playing significant roles. Minority languages like Judeo-Spanish contribute to the cultural tapestry of Morocco. Language policies and education systems aim to promote multilingualism and preserve indigenous languages. The use of English is also growing, particularly in urban areas and within the tourism industry.
Understanding Morocco’s linguistic landscape is crucial for fostering inclusivity and effective communication within the country. It is important for policymakers, educators, and language enthusiasts to recognize and support the diverse languages spoken in Morocco. By valuing and preserving these languages, we can ensure that future generations have access to their cultural heritage while promoting intercultural understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
Morocco has two official languages: Arabic and Berber. These languages hold equal status in the country.
Arabic is the primary language of administration, government, and education in Morocco. It is widely spoken by the majority of the population.
The Berber language, also known as Tamazight, is spoken by a significant portion of the Moroccan population. It has been recognized as an official language alongside Arabic.
French and Spanish have had a considerable influence on Moroccan languages due to historical colonization. Many Moroccans speak French or Spanish as a second language.
Yes, apart from Arabic, Berber, French, and Spanish, there are minor languages spoken in Morocco such as Judeo-Spanish. However, these minority languages are not widely spoken.
The Moroccan education system primarily uses Arabic as the medium of instruction. However, efforts have been made to introduce Berber into some schools to preserve its cultural significance.
According to population census data, linguistic diversity is quite significant in Morocco due to the presence of multiple ethnic groups speaking different languages. This diversity adds richness to Moroccan culture.
Yes, there are online language courses available for learning Arabic and Berber specifically tailored for individuals interested in studying Moroccan languages.
English usage has been increasing steadily over recent years due to its importance for international communication and business purposes. However, it is not as widespread as Arabic or French within the country.
Historically, Morocco has been influenced by various languages due to its geographical location and historical interactions. Arabic, Berber, French, and Spanish have all played significant roles in shaping the linguistic landscape of Morocco.


Leave a Reply