Morocco, known for its vibrant culture and rich history, is generally considered a lower-middle-income country. Poverty in Morocco is prevalent, and the nation struggles with high poverty rates, especially in rural areas. Multiple factors contribute to this issue, including social, economic, and political aspects that impact the lives of its people.
Lack of education and limited job opportunities play a crucial role in perpetuating poverty in Morocco. Despite being part of a rapidly developing world, certain groups within the country still face economic hardships. The rise in poverty rates over the years has been alarming, especially among children. This stark contrast between Morocco’s cultural values and the reality faced by many highlights the need for action.
Join us as we shed light on this pressing issue and discuss potential solutions to uplift those who are most affected.
Historical Perspective of Poverty in Morocco

Economic History
Morocco’s economic history is characterized by a mix of growth and decline. The country has experienced various phases that have shaped its economy over time. In the early 20th century, Morocco was largely agrarian, relying heavily on agriculture for its economic sustenance. However, with the colonization by France and Spain in the early 1900s, there was a shift towards industrialization and modernization.
During the colonial period, Morocco became an important source of raw materials for European powers. This led to the development of industries such as mining, textiles, and manufacturing. Tangier, in particular, emerged as a major trading port connecting Europe and Africa.
After gaining independence from France in 1956, Morocco faced several challenges in building a robust economy. The transition from a colonial economy to an independent one required significant effort and restructuring. The government implemented policies aimed at promoting industrialization and diversifying the economy beyond agriculture.
Policy Shifts
Over the years, policy changes have played a crucial role in shaping Morocco’s economic landscape. The government has recognized poverty as a pressing issue and has taken steps to address it while stimulating overall growth.
In recent decades, there has been a focus on implementing reforms to attract foreign investment and promote private-sector development. These initiatives aim to create job opportunities and reduce poverty levels. Special Economic Zones (SEZs) have been established in regions like Tangier to attract international businesses and foster economic growth.
Furthermore, the Moroccan government has launched various social programs targeting vulnerable populations to alleviate poverty. These programs include cash transfer schemes, healthcare coverage expansion, and educational support initiatives.
The tourism sector also plays a significant role in Morocco’s economy. The country boasts diverse landscapes ranging from bustling cities like Marrakech to picturesque coastal towns like Essaouira. Tourism provides employment opportunities for many Moroccans while contributing significantly to GDP growth.
While Morocco has made progress in reducing poverty rates, challenges remain. The country still faces regional disparities, with rural areas experiencing higher poverty levels compared to urban centers. The issue of unemployment persists, particularly among youth.
Economic Development and Trends
Growth Metrics
Several metrics indicate Morocco’s economic growth. One of the key indicators is the country’s GDP growth rate, which reflects its overall economic performance. Over the years of fighting poverty, Morocco has experienced a positive trend in GDP growth, demonstrating its progress in developing its economy. This growth can be attributed to various factors such as increased investment, both domestic and foreign, and a rise in exports.
Investment plays a crucial role in driving economic growth. By attracting investments from both local and international sources, Morocco has been able to stimulate various sectors of its economy. These investments have contributed to the creation of job opportunities and the development of industries such as tourism, manufacturing, and agriculture.
Furthermore, exports have played a significant role in boosting Morocco’s economic growth. The country has focused on diversifying its export markets and expanding its export base beyond traditional sectors like textiles. This strategic approach has helped increase revenue streams for the country while promoting trade relations with other countries.
Poverty Economic Challenges in Morocco
Despite experiencing positive trends in economic growth, Morocco still faces several challenges that hinder further development. One of the major challenges is high unemployment rates. The country struggles to create enough job opportunities for its growing population, particularly among young people. High levels of unemployment not only impact individuals but also pose social and economic risks for the nation as a whole.
Insufficient infrastructure remains another obstacle to Morocco’s economic progress. While efforts have been made to improve infrastructure across the country, there is still room for further development. Inadequate transportation networks and limited access to basic services can impede business activities and hinder overall economic growth.
To overcome these challenges, Morocco continues to implement policies aimed at fostering sustainable economic development. The government has launched initiatives focused on promoting entrepreneurship and innovation while investing in education and skills training programs to enhance employability.
Agriculture and Industry

Farming Significance
Agriculture plays a significant role in Morocco’s economy. With a diverse range of agricultural products, including cereals, fruits, vegetables, and livestock, the sector contributes to employment and food security. It provides livelihoods for many rural communities and supports their economic development.
The agricultural sector in Morocco has been instrumental in reducing poverty rates by creating job opportunities for farmers and workers. By investing in modern farming techniques and technologies, such as irrigation systems and improved seeds, Morocco has increased its agricultural productivity. This not only ensures food self-sufficiency but also allows for the exportation of surplus produce.
Furthermore, agriculture serves as a vital source of foreign exchange earnings for the country. The exportation of agricultural products like citrus fruits, olives, and fish contributes significantly to Morocco’s revenue streams. By capitalizing on its favorable climate conditions and fertile lands, Morocco has become one of the leading exporters of agricultural goods in Africa.
Industrial Contribution
Alongside agriculture, the industrial sector is an important driver of Morocco’s economy. Manufacturing industries have experienced substantial growth over the years, contributing to GDP expansion and job creation. The automotive sector stands out as one of the key pillars of Morocco’s industrialization efforts.
Morocco has attracted major international automakers who have established production plants within the country. This strategic move has not only led to job opportunities but also promoted technology transfer and skills development among local workers. As a result, Morocco has positioned itself as an automotive hub in North Africa.
In addition to manufacturing industries, mining also plays a crucial role in driving economic growth in Morocco. The country possesses significant mineral resources such as phosphates, which are used extensively in fertilizers. By leveraging these resources through responsible mining practices, Morocco benefits from both domestic consumption and exportation.
Industrialization efforts have allowed Morocco to diversify its exports beyond traditional sectors like agriculture. This diversification enhances the country’s resilience to external shocks and fosters economic stability. By expanding its industrial base, Morocco has strengthened its position in global markets and attracted foreign direct investment.
Services and Tourism

Tourism Revenue
Tourism plays a crucial role in driving Morocco’s economy against poverty. As one of the largest sectors, it generates significant revenue for the country. With its diverse landscapes, rich history, and vibrant culture, Morocco attracts millions of international visitors each year.
The tourism industry in Morocco has experienced steady growth over the years. Investments in infrastructure, such as hotels, resorts, and transportation networks, have been instrumental in supporting this growth. These developments have made it easier for tourists to explore Morocco‘s attractions and contributed to increased visitor numbers.
The revenue generated from tourism has a positive impact on various aspects of the Moroccan economy. It creates job opportunities for locals and stimulates economic activity in related industries such as hospitality, food services, and transportation. The influx of tourists also boosts local businesses by increasing demand for products and services.
Service Economy
In addition to tourism, Morocco’s service sector is a vital component of its economy. Services like finance, telecommunications, retail, and tourism-related activities contribute significantly to the country’s growth.
The finance sector plays a crucial role in providing banking services to individuals and businesses alike. It facilitates investments and supports economic development by offering loans and financial solutions. This sector also helps attract foreign direct investment (FDI) into Morocco.
Telecommunications is another important service industry that drives economic growth. With advancements in technology and increased internet penetration rates across the country, telecommunication companies have expanded their offerings to meet growing demands. This expansion has not only improved connectivity but also created employment opportunities for many Moroccans.
The retail sector also contributes to Morocco’s service-oriented economy. The rise of modern shopping malls and retail outlets has transformed the way people shop in the country. These establishments provide a wide range of products from both local and international brands, catering to diverse consumer needs.
International Trade and Investment
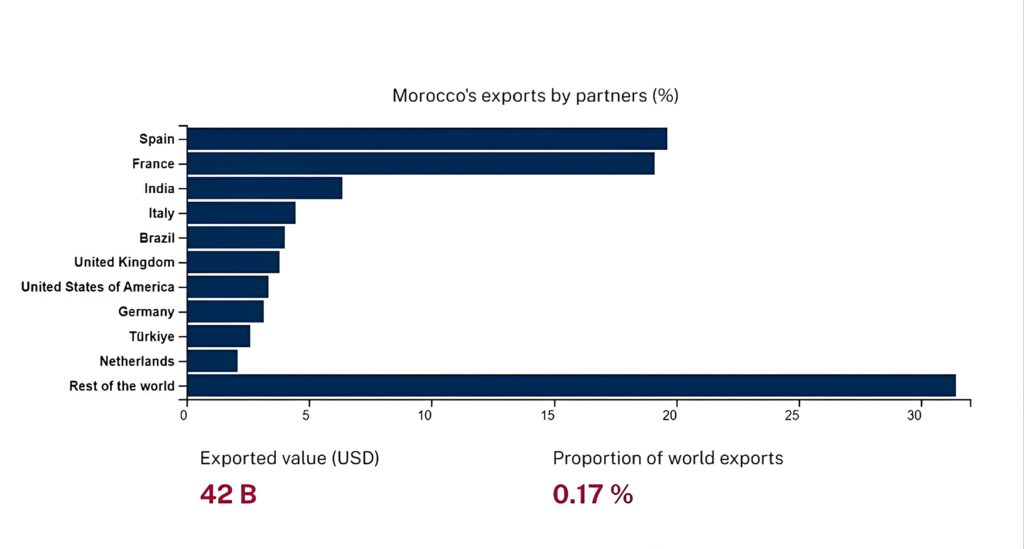
Trade Partners
Morocco has established diverse trade partnerships that contribute to its economic growth. One of the significant trading partners for the country is Europe. Through various trade agreements, Morocco has fostered economic cooperation with European countries, resulting in increased exports and imports.
The trade agreements between Morocco and European nations have facilitated the exchange of goods and services, creating opportunities for businesses in both regions. This partnership has allowed Moroccan companies to access larger markets and benefit from international standards and practices.
Morocco has expanded its trade relations beyond Europe. The country has entered into agreements with other countries worldwide, including the United States, China, and several African nations. These agreements promote bilateral trade by reducing barriers such as tariffs and quotas.
By diversifying its trade partnerships, Morocco reduces its dependence on a single market, making its economy more resilient to external shocks. Furthermore, these partnerships open up avenues for collaboration in various sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, tourism, and renewable energy.
Foreign Investment
Foreign investment plays a crucial role in boosting Morocco’s economy. The country actively encourages investments from abroad through government incentives and favorable business conditions. These investments contribute to job creation, technology transfer, infrastructure development, and overall economic growth.
Morocco offers attractive incentives to foreign investors such as tax breaks, financial assistance programs, streamlined administrative procedures, and access to special economic zones. These measures aim to attract businesses from different sectors including automotive manufacturing, aerospace industry, renewable energy projects, information technology services, and tourism.
Foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows have been instrumental in driving Morocco’s industrialization efforts. Many multinational corporations have established production facilities or regional headquarters in the country due to its strategic location at the crossroads of Africa and Europe.
Moreover, FDI inflows have helped develop key sectors such as automotive manufacturing where global companies have set up plants in Tangier’s free zone area. This has created employment opportunities for the local population and stimulated economic growth in the region.
Infrastructure Development

Transportation
Efficient transportation systems play a vital role in the economic development of any country. The government has recognized the importance of investing in infrastructure projects to improve connectivity within the country and beyond. These investments have resulted in significant advancements in transportation, benefiting both trade and tourism.
Morocco has made substantial progress in enhancing its transportation networks, particularly through the development of ports, railways, and roads. The country’s strategic location as a gateway between Europe and Africa makes it an ideal hub for international trade. The construction of modern ports such as Tanger-Med has significantly increased Morocco’s capacity to handle cargo and facilitate import-export activities.
Moreover, the expansion of railway networks has improved accessibility across different regions of the country. The high-speed rail line connecting Casablanca with Tangier reduces travel time and promotes economic integration between these major cities. Ongoing infrastructure projects aim to extend railway lines to other areas, further improving connectivity within Morocco.
Investments in road infrastructure have also been crucial for facilitating transportation across the country. The construction of highways and expressways has enhanced mobility for both people and goods. For instance, the completion of the A2 highway project linking Rabat with Fes has reduced travel time between these cities by half.
Communication Networks
Reliable communication networks are essential for supporting economic activities in Morocco. Access to telecommunications services enables businesses to connect with customers and partners efficiently. It plays a crucial role in promoting trade, attracting foreign investment, and fostering innovation.
The Moroccan government recognizes the significance of expanding internet connectivity to promote digital inclusion among its citizens. Efforts have been made to increase access to broadband internet services throughout the country, including in rural areas. This expansion allows businesses operating outside major urban centers to leverage digital technologies effectively.
Improving communication networks also benefits various sectors such as education and healthcare. With reliable internet access, students can access online educational resources and participate in distance learning programs. Similarly, telemedicine services can reach remote areas, providing healthcare access to underserved communities.
Economic Inequality and Labor Issues
Income Disparity
Income disparity is a significant challenge in Morocco. The gap between the rich and poor remains wide, contributing to the country’s overall poverty levels. While some individuals enjoy high incomes and luxurious lifestyles, many others struggle to make ends meet. This stark contrast in wealth distribution highlights the need for measures to address income inequality.
Reducing income disparity is crucial for poverty reduction in Morocco. By implementing policies that promote fairer wealth distribution, the government can help uplift those living in poverty and create a more equitable society. These policies may include progressive taxation systems, social welfare programs, and targeted initiatives to support marginalized communities.
Unemployment Concerns
High unemployment rates pose significant challenges to Morocco’s economy. One of the most pressing issues is youth unemployment, which disproportionately affects young people seeking job opportunities after completing their education or training. The lack of employment prospects can lead to frustration and disillusionment among the youth population.
To combat unemployment, job creation initiatives are essential. The Moroccan government has been working on implementing various programs aimed at generating employment opportunities across different sectors of the economy. These initiatives focus on supporting entrepreneurship, promoting vocational training programs, and attracting foreign investment to create jobs.
Efforts are also being made to improve labor market conditions by enhancing worker protection rights and ensuring fair wages for all employees. By addressing these labor issues, Morocco aims to foster a more inclusive economy that provides equal opportunities for all its citizens.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Resource Management
Effective resource management is essential for sustainable development in Morocco. The country faces challenges related to water scarcity, which affects both agriculture and industry. With limited freshwater resources, Morocco has implemented various strategies to ensure the efficient use of water. These include the construction of dams and reservoirs for water storage, as well as the implementation of irrigation systems that optimize water usage.
In addition to addressing water scarcity, Morocco is also focused on diversifying its energy production. The country has made significant progress in harnessing renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. The Noor Ouarzazate Solar Complex, for example, is one of the world’s largest concentrated solar power plants. It can generate electricity even after sunset using thermal energy storage technology.
Conservation Efforts
Environmental conservation efforts play a crucial role in promoting sustainability in Morocco. The preservation of natural resources supports long-term economic growth while protecting biodiversity and ecosystems. To achieve this, the country has implemented various initiatives aimed at preserving its rich natural heritage.
One such initiative is focused on biodiversity preservation. Morocco is home to diverse ecosystems, including forests, wetlands, and coastal areas that are vital habitats for numerous plant and animal species. Efforts are being made to protect these ecosystems through the establishment of protected areas and national parks.
Morocco is also committed to increasing its adoption of renewable energy sources as part of its conservation efforts. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, the country aims to mitigate climate change while ensuring a sustainable future for its citizens. Initiatives have been launched to promote renewable energy projects such as wind farms and solar power plants across different regions in Morocco.
Regional Development Disparities

Urban vs Rural
In Morocco, there exists a significant divide between urban and rural areas in terms of economic development. Urban areas, such as major cities like Casablanca and Marrakech, offer more employment opportunities and access to services compared to rural regions. The concentration of industries, businesses, and infrastructure in urban centers attracts investment and drives economic growth.
Urban areas benefit from a diverse range of sectors including finance, tourism, manufacturing, and services. These sectors provide job opportunities for the local population and contribute to the overall economic prosperity of the region. Urban areas have better access to education, healthcare facilities, transportation networks, and other essential services that support socio-economic development.
On the other hand, rural areas face several challenges that hinder their economic progress. Limited job opportunities lead to higher unemployment rates in these regions. The lack of basic infrastructure such as roads and schools further exacerbates the disparities between urban and rural communities. As a result, many individuals from rural areas migrate to cities in search of better livelihoods.
To address this urban-rural divide and reduce regional disparities in Morocco’s economy, various rural development programs have been implemented. These programs aim to promote sustainable agriculture practices, improve access to credit for farmers, enhance infrastructure development in rural areas such as irrigation systems and roads, and provide vocational training opportunities for young people.
Regional Policies
Regional policies play a crucial role in shaping economic development across different parts of Morocco. The government has initiated various policies that focus on promoting growth in specific regions by leveraging their unique strengths or addressing specific challenges they face.
For example, the “Plan Maroc Vert” (Green Morocco Plan) aims to develop sustainable agriculture practices across different regions of the country. This initiative focuses on improving agricultural productivity through modernization techniques while also ensuring environmental sustainability.
Another notable regional policy is the “Industrial Acceleration Plan,” which targets specific industrial zones outside major cities. By providing incentives and support to businesses in these regions, the government aims to attract investment, create job opportunities, and stimulate economic growth outside urban centers.
Furthermore, regional cooperation plays a vital role in enhancing trade and investment opportunities. Collaborative initiatives between neighboring regions or countries can lead to the development of cross-border economic zones, which facilitate trade flows and encourage investments.
Poverty Rate Trends and Future Steps in Morocco
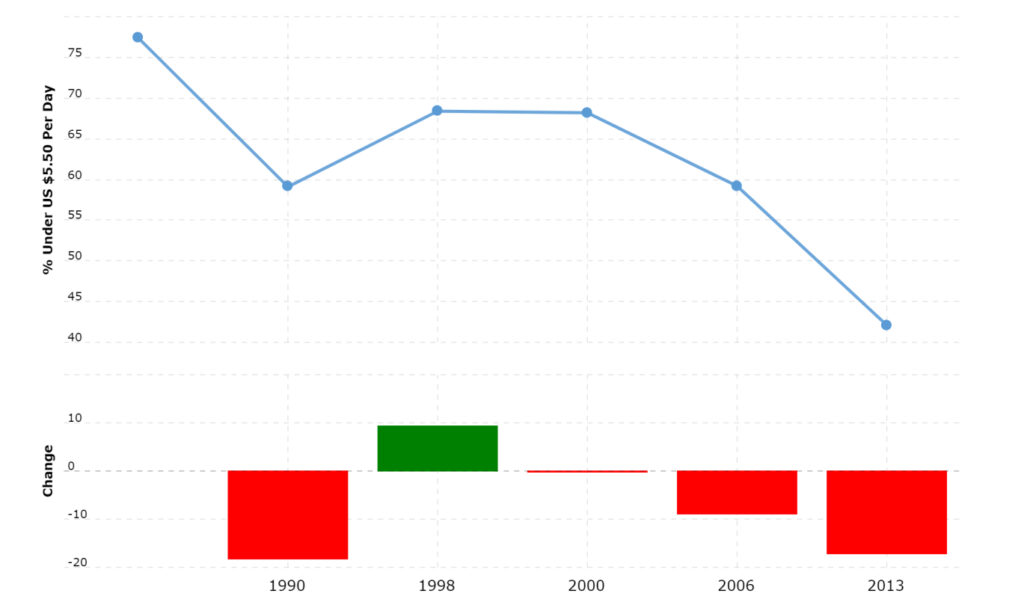
Current Statistics
Recent statistics provide valuable insights into Morocco’s economy, shedding light on key indicators such as GDP, inflation rate, and poverty rates. Analyzing this data is crucial for assessing the country’s economic performance and understanding its poverty situation.
Morocco has made significant progress in reducing poverty over the years. According to the World Bank, the national poverty rate declined from 15.3% in 2007 to 4.8% in 2019. This reduction indicates a positive trend towards alleviating poverty and improving living conditions for many Moroccans.
Moreover, Morocco’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) has been steadily growing, reaching $119 billion in 2020. This economic growth reflects the nation’s efforts to diversify its economy and attract foreign investments across various sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, tourism, and renewable energy.
While these statistics demonstrate positive developments in Morocco’s economy, it is important to note that challenges persist. Inflation remains a concern due to rising food prices and external factors like global market fluctuations. High inflation can hinder the purchasing power of individuals and exacerbate poverty levels if not effectively managed.
Reduction Strategies
To address poverty effectively, Morocco has implemented various strategies aimed at reducing inequality and supporting vulnerable populations. Social welfare programs play a crucial role in assisting those in need.
The National Initiative for Human Development (INDH) is one such program that focuses on enhancing access to basic services like healthcare, education, housing, and clean water for marginalized communities. Through its targeted interventions, INDH aims to uplift individuals out of poverty by addressing their immediate needs while promoting long-term sustainable development.
Economic diversification is vital in reducing dependency on specific industries or sectors that may be prone to volatility or stagnation. By expanding into new areas such as renewable energy production and digital innovation, Morocco aims to create more job opportunities and stimulate economic growth across different regions.
Efforts to promote job creation are also crucial in combating poverty. The Moroccan government has implemented initiatives like the National Initiative for Human Development and the Industrial Acceleration Plan to foster entrepreneurship, attract investments, and support small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). These measures aim to create a favorable business environment that encourages innovation, job creation, and economic prosperity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Morocco’s journey towards reducing poverty has been marked by significant progress and challenges. The country has made commendable strides in economic development, particularly in sectors such as agriculture, industry, services, and tourism. However, there are still disparities in regional development and persistent issues of economic inequality and labor concerns that need to be addressed.
To further combat poverty, Morocco must focus on sustainable development and environmental impact. By promoting green initiatives and ensuring the longevity of natural resources, the country can not only uplift its citizens but also contribute to a healthier planet.
As you reflect on this exploration of poverty in Morocco, consider how you can contribute to the cause. Whether it’s supporting local businesses, advocating for fair labor practices, or engaging in responsible tourism, your actions can make a difference. Together, we can strive towards a more equitable and prosperous future for all.
Frequently Asked Questions
Morocco is not considered a poor country. While it faces challenges with poverty and inequality, the country has made significant progress in economic development and poverty reduction over the years.
Morocco’s economy has experienced growth and diversification, with sectors like agriculture, industry, services, and tourism contributing to its development. The government has implemented various policies to promote economic stability and attract foreign investment.
Agriculture plays a crucial role in Morocco’s economy, employing a significant portion of the population and contributing to GDP. The sector is vital for food security, rural development, and export earnings of products such as citrus fruits, vegetables, and cereals.
Tourism is a key contributor to Morocco’s economy. The country boasts diverse attractions like historical sites, vibrant cities, beautiful landscapes, and cultural heritage. Tourism generates revenue through accommodation services, transportation, restaurants, and the sale of handicrafts.
Morocco has implemented various initiatives to reduce poverty rates. These include social programs targeting vulnerable populations, investments in education and healthcare systems, job creation efforts through economic reforms, and regional development projects aimed at reducing disparities among different areas of the country.


Leave a Reply